Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager (GTM) manages tags that are used for tracking and analytics on websites. GTM can be leveraged as a way to integrate the Harness FME Browser SDK in a site and reference it from other custom tags.
Automatic tracking for events defined on GTM and gtag.js
When you use Google Tag Manager for tracking and analytics, which is powered by Google Universal Analytics (GA) library, you can configure the FME SDK's Google Analytics (GA) integration to automatically track these events (or a desired subset) into Harness FME to feed our stats engine.
To integrate Harness FME's Google Analytics to Split integration, configure the integration when you instantiate the SDK and a GA plugin, which is required for your selected trackers. This allows you to pick up events that are generated and processed by GA (with multiple customization options) and send the events to Harness FME.
When you use Google Tag Manager or Global Site Tag (gtag.js) to set up your Universal Analytics configuration, trackers are created with dynamic names.
To do this, you need to require the splitTracker plugin for the desired trackers. However, because their names are unknown when writing the code, doing it manually by placing the command ga('<trackerName>.require', 'splitTracker') won't work. Instead, include the autorequire script created for this integration after your GTM/gtag.js tag, which integrates with the ga command queue and handles the corresponding require commands for the Harness FME plugin automatically.
<!-- Google Tag Manager -->
<script>
(function(w,d,s,l,i){w[l]=w[l]||[];w[l].push({'gtm.start':
new Date().getTime(),event:'gtm.js'});var f=d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0],
j=d.createElement(s),dl=l!='dataLayer'?'&l='+l:'';j.async=true;j.src=
'https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtm.js?id='+i+dl;f.parentNode.insertBefore(j,f);
})(window,document,'script','dataLayer','GTM-XXXXXXX');
</script>
<!-- You can include it from our CDN -->
<script src="//cdn.split.io/sdk/ga-to-split-autorequire.js"></script>
<!-- Alternatively, you can copy the content of that file inside a script tag and it would be equivalent -->
<!-- <script>
// Paste here the content of https://cdn.split.io/sdk/ga-to-split-autorequire.js
</script> -->
<!-- Global site tag (gtag.js) -->
<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-XXXXXXXX-1"></script>
<script>
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', 'UA-XXXXXXXX-1');
</script>
<!-- You can include it from our CDN -->
<script src="//cdn.split.io/sdk/ga-to-split-autorequire.js"></script>
<!-- Alternatively, you can copy the content of that file inside a script tag and it would be equivalent -->
<!-- <script>
// Paste here the content of https://cdn.split.io/sdk/ga-to-split-autorequire.js
</script> -->
Injecting the Harness FME SDKs through a GTM tag
You can leverage GTM as a way to integrate the Harness FME Browser SDK in a site and reference it from other custom tags. By using the FME JavaScript SDK (the one used on this example) or the Browser SDK, Harness FME can be integrated with Google Tag Manager with minimal effort. This methodology works with both UA and GA4.
Sending FME to Google Tag Manager's data layer
The best approach to obtaining a reference to the FME SDK factory client within Google Tag Manager is to utilize the data layer, as this keeps us from cluttering the global variable namespace. To achieve this, add a line to the FME SDK initialization code on the HTML page to push the FME SDK factory client to the data layer. The code below sets the data layer variable split_client to the FME client instance.
<script>
// ...
var factory = splitio({
// FME SDK initialization config goes here
});
var client = factory.client();
// ...
// Push the SDK factory client to the data layer
dataLayer.push({ split_client: client });
</script>
Assigning the FME SDK factory client to a variable within Google Tag Manager
After you utilize the data layer, we define a new variable within Google Tag Manager called Split Client set to the data layer variable split_client. This enables us to reference the FME SDK factory client within our tags in Google Tag Manager.
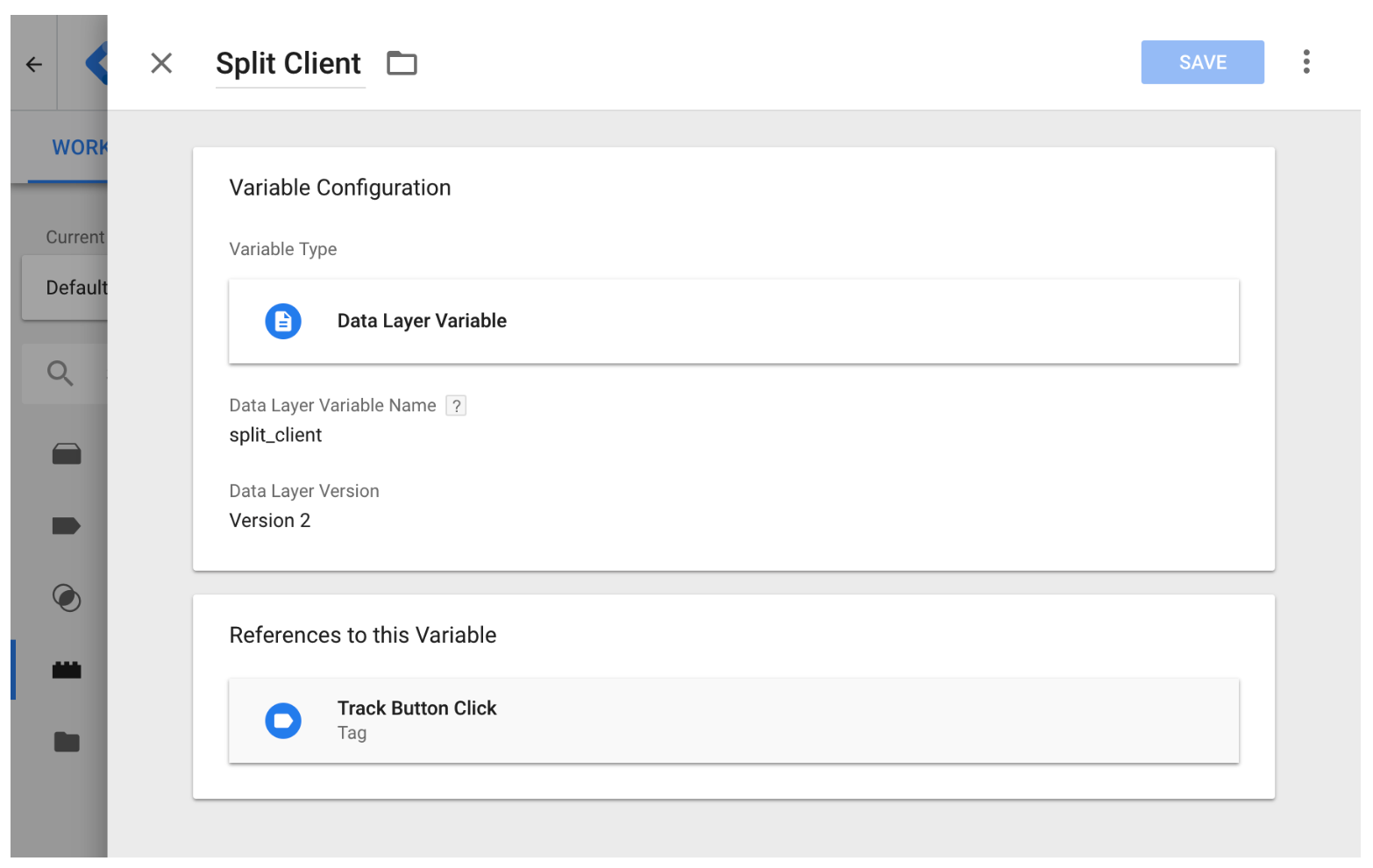
Referencing the FME SDK factory client in tags within Google Tag Manager
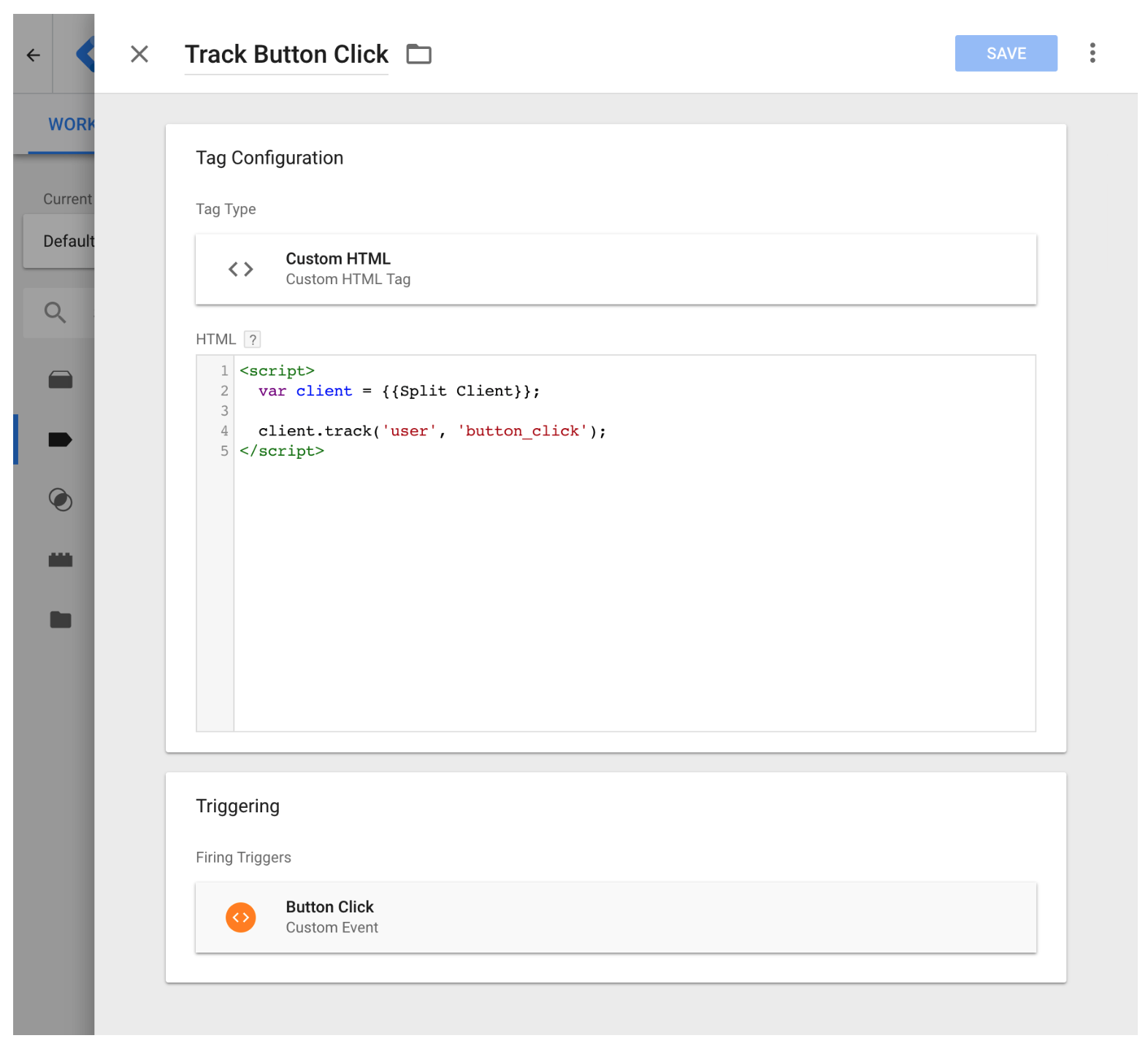
Once you define the new variable, we create a new custom HTML tag which includes our JavaScript code that references the FME SDK factory client. For this example, we perform a simple track call which logs an event to Harness FME. We are setting the local variable client to the Google Tag Manager variable
{{Split Client}} we defined in the previous step so we can access our FME SDK factory client within the tag.
<script>
var client = {{Split Client}};
// ...
</script>
As we add other tags to Google Tag Manager, we always want to repeat this pattern of first setting the local variable client to the Google Tag Manager variable {{Split Client}}.
Advanced topics
This section describes advanced use cases and features.
Initializing the FME SDK within Google Tag Manager
For most users, initializing the FME SDK on the HTML page and then pushing the client to the data layer is the best approach as it allows the FME SDK factory client to be accessible within both environments and avoids race conditions. For installations that don't need to access the FME client within the code on the HTML page or do not mind how Google Tag Manager loads in scripts asynchronously, another viable option is to initialize the FME client within Google Tag Manager.
You can initialize the FME SDK by inserting the following code into a custom HTML tag which fires on all pages:
<script>
// ...
var factory = splitio({
// FME SDK factory initialization config goes here
});
var client = factory.client();
// ...
// Push the SDK factory client to the data layer
dataLayer.push({ split_client: client });
</script>
You can now add your variables and tags as suggested in the previous sections.
Be aware that this tag must fire before any other tags which reference the FME SDK factory client or you can run into race conditions where the FME client variable is undefined. To learn about how to address this, refer to Google's documentation on Tag Sequencing in Google Tag Manager.